1. PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT EC – AUSTRIA 2021 - 2027
The partnership agreement with Austria covers 5 funds: ERDF, ESF+, Cohesion Fund, Just Transition Fund and the European Maritime, Fisheries and Aquaculture Fund (EMFAF)On the 2nd of May 2022, the Commission published its Partnership Agreement with Austria, which is a €1.3 billion cohesion policy investment strategy for the period 2021-2027.
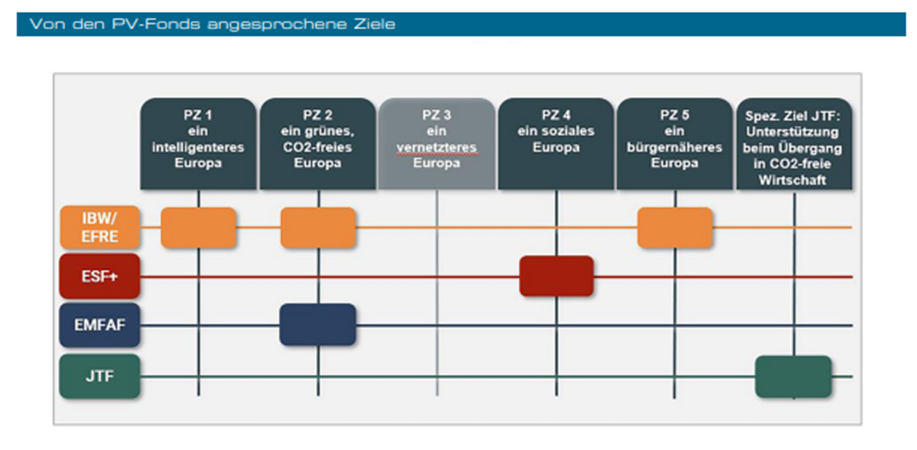
A. INTRODUCTION ERDF AND ESF+ 2021 - 2027
- Improved productivity and competitiveness of companies through innovation projects and the adoption of state of the art & digital technologies
- Reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions by promoting investments in more resource and energy efficiency, as well as integral consideration of the circular economy
- Increasing the quality of the environment, air and quality of life in cities and urban environs via integrated concepts for sustainable urban development and resource-saving land development
- Implementation of integrated regional development via the CLLD approach in Tyrol for promotion of integrated social, economic and environmental development
-> ERDF programs:
- Programm IBW-EFRE/JTF 2021–2027: Europäischer Fonds für Regionale Entwicklung: IBW-EFRE/JTF 2021–2027: Investitionen in Beschäftigung, Wachstum und den Übergangzueiner CO2-armen Wirtschaft in Österreich 2021–2027
- Measures that address the unequal distribution of income (including the low-wage sector): (Further) development of company-related approaches, qualification, professional training
- Regional and sector-specific approaches that support the compatibility of work and care tasks (e.g. childcare): innovative, regional approaches (e.g. networks between communities, companies and stakeholders, advice on re-entry)
- Measures to break down stereotypes: approaches to promoting gender-neutral career choices, Qualification, campaigns, pilot projects for/with target groups that have not been reached so far.
- ESF+ ProgrammBeschäftigungÖsterreich & JTF 2021-2027
- ESF+ Programm zur Bekämpfung materieller Deprivation 2021-2027
2. POLICY CHOICES
- Europäischer Fonds für Regionale Entwicklung – EFRE, Programm IBW/EFRE & JTF 2021-2027 – Investitionen in Beschäftigung, Wachstum und den Übergangzueiner CO2-armen Wirtschaft in Österreich 2021-2027 (Investments in employment, growth and the Transition to a low-carbon economy in Austria 2021-2027)
Justification for choice PO: Despite positive macroeconomic developments before the Covid-19 pandemic, the multi-factor productivity (MFP) showed that in a European comparison, Austria has a high level of labor productivity but multi-factor productivity (MFP) has grown more slowly than in other European countries since the financial and economic crisis (OECD, 2018). The interventions also address the challenge of increased participation in the European Research Area. Moreover, there will be a focus on SMEs, more specifically upgrading the existing skills and specializations. “Digitization” will be an integral topic of the program due to its high importance and will be supported by research and innovation projects.
- ProgrammBeschäftigungÖsterreich 2021-2027 & JTF – EuropäischerSozialfonds- ESF+
- ESF+ ProgrammzurBekämpfungmaterieller Deprivation 2021-2027
- The European Pillar of Social Rights was adopted by the European Council in autumn 2017, which in the “Social Protection and Social Inclusion” section contains the special principle for the protection of includes children from poverty.
- The European Child Guarantee, adopted by the Council of the European Union on June 14, 2021, aims to ensure that every child at risk of poverty in Europe has access to fundamental rights like health and education gets.
- The results of the mid-term evaluation of the Fund for European Aid to the Most Deprived, including the results of the stakeholder interviews recognize that the fund’s material support and social inclusion measures help the target groups in a real way.
3. LINK TO SOCIAL SERVICES – OBJECTIVES RELEVANT TO SOCIAL SERVICES
4. USEFUL RESOURCES
The Partnership agreement between AT and the Commission: https://ec.europa.eu/info/publications/partnership-agreement-austria-2021-2027_en
Information on the PA: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/da/ip_22_2726
ESF+ in Austria: https://www.esf.at/en/esf-in-oesterreich-2/
ERDF in Austria: https://www.efre.gv.at/en#:~:text=In%20the%202014%2D2020%20funding,or%20provincial)%20co%2Dfinancing.
Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.




