General information
The profile below has been designed on the basis of the Partnership Agreement approved by the European Commission on 25 May 2022.
It includes 4 national programs (ERDF, ESF+, JTF, EMFAF) and 8 regional programs (program for Stockholm, program for Eastern Central Sweden, program for Småland and the islands, program for Skåne-Blekinge, program for Western Sweden, program for Northern Central Sweden, program for Middle Norrland, program for Upper Norrland).
Chosen policy objective 4: A more social and inclusive Europe through the implementation of the European Pillar of Social Rights
The country-specific recommendations for Sweden 2019 concerned, among other things, investments to improve the educational systems’ effectiveness and labor market relevance, as well as the need for investments to support the integration of those born abroad and promote active inclusion and improve the employability of less advantaged people.
The consequences of the covid-19 crisis have strongly affected the situation on the labor market. Anyone who has lost their job needs good opportunities to change to a new job. The efforts within React-EU are therefore focused on women and men who have become unemployed during the pandemic and need arming and matching efforts to strengthen their position on the labor market and quickly get to work. The efforts are also aimed at employed people who are judged to need skills development in order to strengthen their position on the labor market.
Increased unemployment can also cause higher long-term unemployment. Even before the pandemic, long-term unemployment was high. Groups that have previously been excluded or have a weak position on the labor market risk being hit particularly hard. The pandemic has contributed to accelerating the structural transformation of the labor market.
Digitization and automation are becoming increasingly important, which places new demands on the workforce’s skills and that there are opportunities for skill development, training and change.
The program contains skills-enhancing and individually tailored efforts so that jobseekers can strengthen their position on the labor market and take the jobs that come. The program also includes measures that ensure that the matching to industries with continued significant recruitment needs works well.
The program includes lifelong learning with opportunities for guidance, validation, competence development and retraining. It improves the conditions for mobility on the labor market and for employees to be able to maintain their position on the labor market as the demands of working life develop, for example as a result of digitization or the green transition. It is important that the education system provides flexible opportunities for education for different target groups, in order to meet the needs of both the unemployed and employees for skills development and retraining. The program includes efforts to meet identified challenges in the field of education, including for more individuals to complete regular education at primary, secondary and post-secondary level. Competence supply initiatives are carried out based on the needs of the labor market.
The income differences between those with the highest and lowest incomes have increased, while real incomes have increased in all groups. Absolute poverty has decreased and in Sweden the percentage of absolute poor is the lowest in the EU. However, relative poverty has increased slightly over the past ten years. The proportion of people receiving support has decreased slightly, but the amount of support paid has increased slightly between 2010 and 2019. In order to strengthen social inclusion and reduce material poverty, there are efforts to get people closer to the labor market. Thus, the possibility of self-sufficiency can be increased. In order to break social exclusion and fight poverty, there are initiatives for children that increase the possibilities for long-term inclusion in society. The efforts for financially disadvantaged children aim to strengthen their schooling, create meaningful free time and inclusion in the social community.
Middle Norrland and Upper Norrland take part in special funds as there are challenges in the form of large distances and a low population density. The program therefore has special distance-bridging and capacity-building efforts in these program areas. The efforts are primarily aimed at strengthening the capacity of local and regional structures, but can also be directed at individuals.
The measures contribute to the implementation of the European Pillar of Social Rights, in particular the principles of active labor market measures, education and lifelong learning, gender equality and equal opportunities.
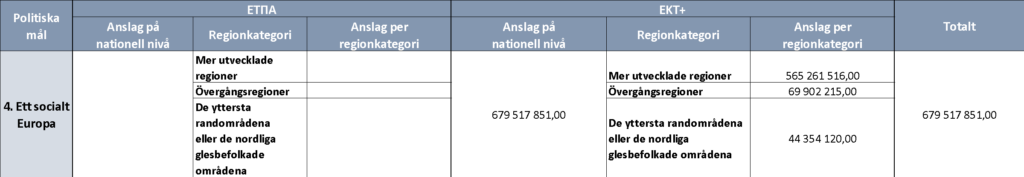
Preliminary grant from ERDF and ESF+ per political objective
Thematic concentration

European Social Fund+ (ESF+)
Within political objective 4, the national program for ESF+ must contain actions that lead to improving access to employment, promoting lifelong learning, encouraging active inclusion and promoting social inclusion. The focus is on strengthening and preventive efforts for the individual as well as on efforts that long-term test, develop and strengthen methods, etc. at organizational and structural level. ESF+ in Sweden is a national program with eight regional action plans.
The largest part of the national program is directed to program area A and shall contribute to employment, growth and a sustainable working life both through lifelong learning and by increasing the opportunity for employment or studies for all jobseekers. Within program area B, funds are allocated to Arbetsförmedlingen for initiatives that contribute to transitions to work or studies. The efforts should contribute to individuals who are far from the labor market getting into work or closer to the labor market. Within program area C, efforts are aimed at supporting individuals who are financially vulnerable within the definition of relative poverty. The efforts must also counteract and mitigate the consequences of child poverty. In order to increase capacity in Upper Norrland and Middle Norrland, program area D will contain efforts that contribute to modernizing the labor market’s institutions and services. Within program area E, efforts are carried out to contribute to the development, testing, implementation and dissemination of social innovations.
The funds within ESF+ must be directed where they do the most good in society. Through efforts that develop national policy, ESF+ must create added value and complement national efforts, e.g. interventions for individuals far from the labor market, such as foreign-born women and young people who neither work nor study, and interventions for individuals in need of transition to a new profession. Efforts can be carried out in areas where EU funding contributes to Sweden being able to do more for the target group for ESF+ so that more individuals develop and get closer to the labor market or are given the opportunity to remain in the labor market.
A more social and inclusive Europe
Within political objective 4, ESF+ shall improve access to employment, promote lifelong learning, encourage active inclusion and promote social inclusion, and for the northernmost program areas also contribute to modernizing labor market institutions and services.
Developing skills for smart specialisation, structural transformation and entrepreneurship is a specific objective within the ERDF. To contribute to this specific goal, the ERDF can support strategic skills supply work in small and medium-sized companies in areas linked to smart specialization.
Cooperation in ESF+ can also be relevant in relation to Erasmus+ and the European Solidarity Corps, where synergies can be about promoting mobility for educational purposes for students with poorer conditions or participating in volunteer activities, strategic partnerships, youth exchanges and skills development for people who work with young people.
Inclusion and integration in the labor market are required to achieve sustainable economic growth. The countries around the Baltic Sea face similar challenges regarding aging population, skills gap, lifelong learning, transition between education and working life and getting young people to complete their upper secondary education. ESF+ enables the efforts of various actors within the Baltic Sea Strategy through, among other things, project calls.
When it comes to increasing the skills and retraining of workers, ESF+ can support efforts throughout the country, while FRO only supports such efforts linked to the climate transition for the steel industry in Norrbotten County and the metal industry in Västerbotten County. Efforts within the ERDF (political objective 1) and ESF+ can complement efforts within FRO in terms of skill enhancement and retraining of workers. ESF+ also supports efforts for jobseekers who are far from the labor market and can thereby supplement FRO, which in Sweden is aimed at employees.
To enable regions and people to deal with the social, employment-related, economic and environmental consequences of the transition towards the Union’s energy and climate targets for 2030 and a climate-neutral economy in the Union by 2050, building on the Paris Agreement.
Efforts within the ERDF (political objective 1) and ESF+ can complement efforts within FRO in terms of increasing the skills and retraining of workers in the manner shown above.
The aim of the Asylum, Migration and Integration Fund (Amif) is to contribute to the effective management of migration flows and to the implementation, strengthening and development of the common asylum and migration policy. Amif can complement the Fund for Integrated Border Management, the Instrument for Border Control and Visas (BMVI) with the development of integrated border management, where one of the components concerns return. Amif can also supplement ESF+ in terms of integration measures – language training, social orientation and work preparation measures. Amif can carry out initiatives early in the integration process for those born abroad, while ESF+ has a longer-term perspective.
The EU Internal Security Fund (ISF) aims to ensure a high level of security within the Union, in particular by preventing and combating terrorism and radicalisation, serious organized crime and cybercrime and providing support to victims of crime. There may be opportunities for synergies between ISF and ESF+ to counter radicalization by promoting social inclusion.
Useful links
- Your guide to EU programs in Sweden
https://eufonder.se/om-eufonder.se/in-english.html
- A compilation of the 26 programs within the European Structural and Investment Funds, the ESI funds, which affect Sweden, and in which programs Swedish organisations, authorities and companies can participate.
- National Single website portal
Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.




